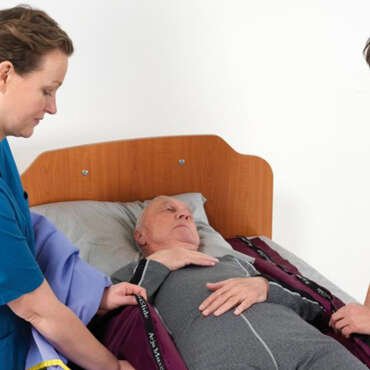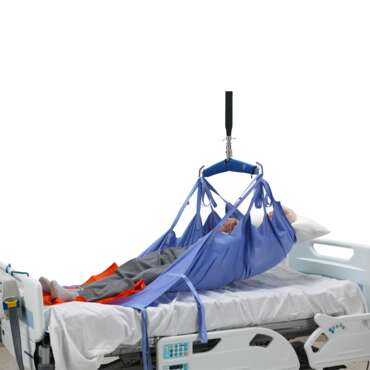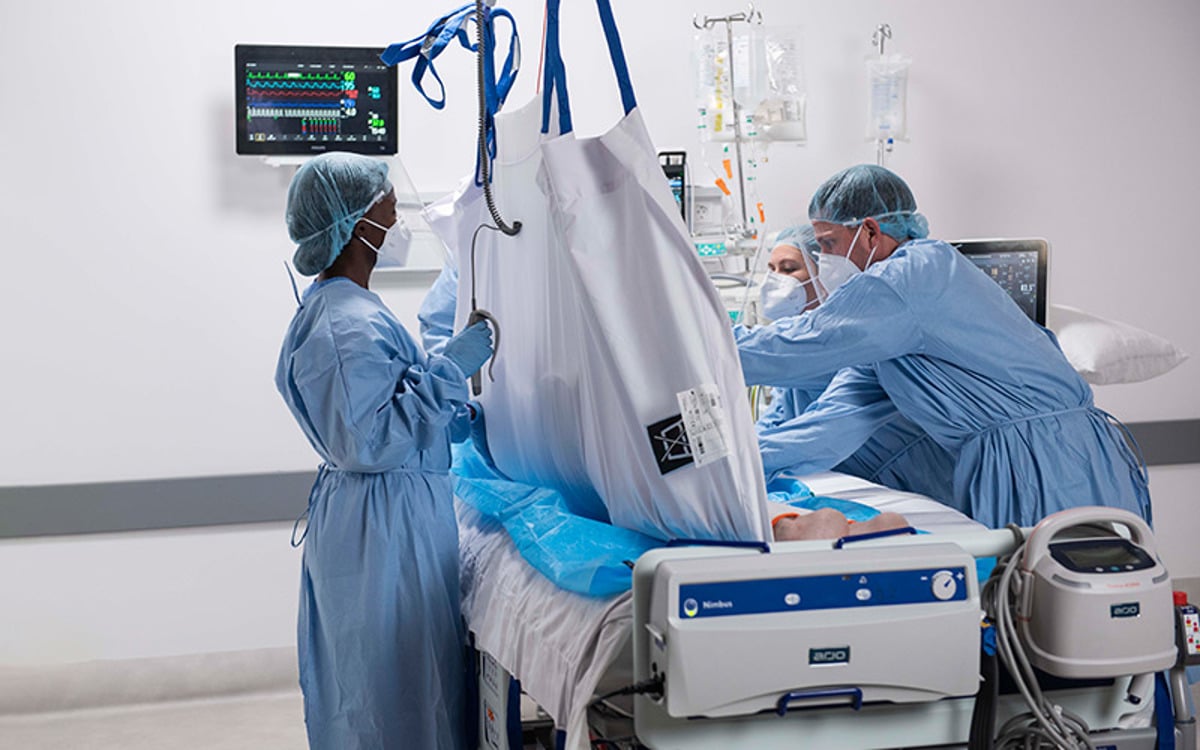
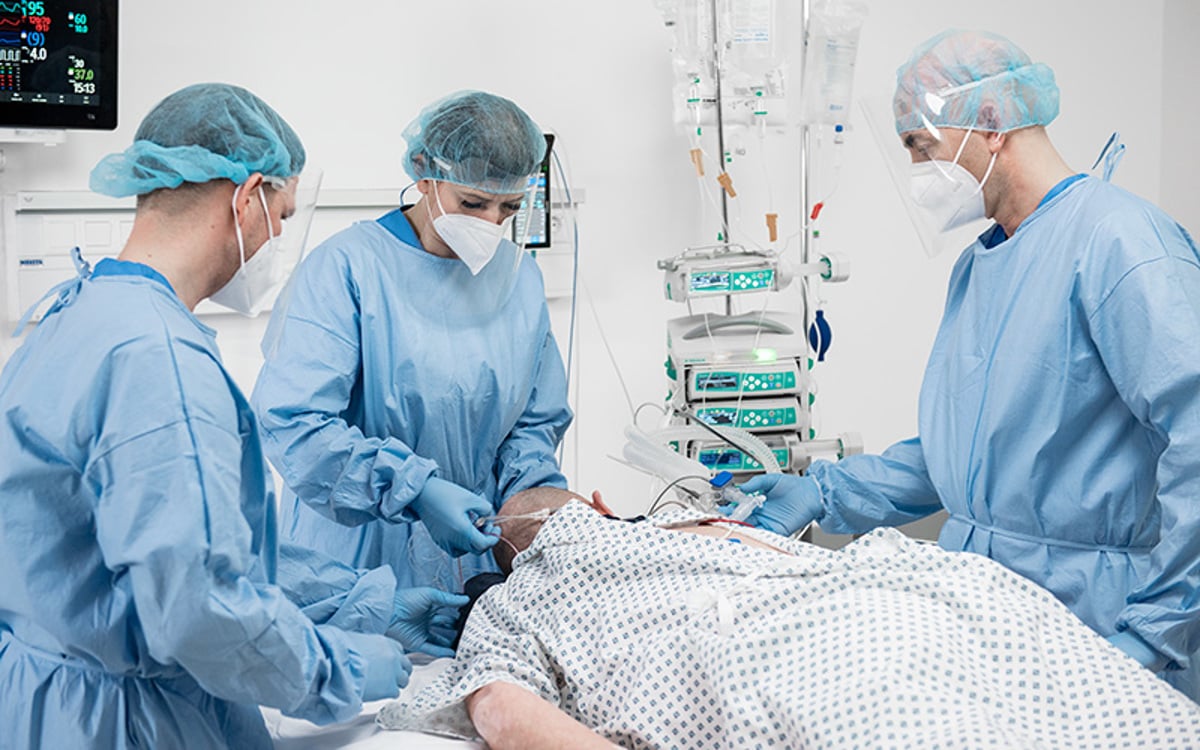
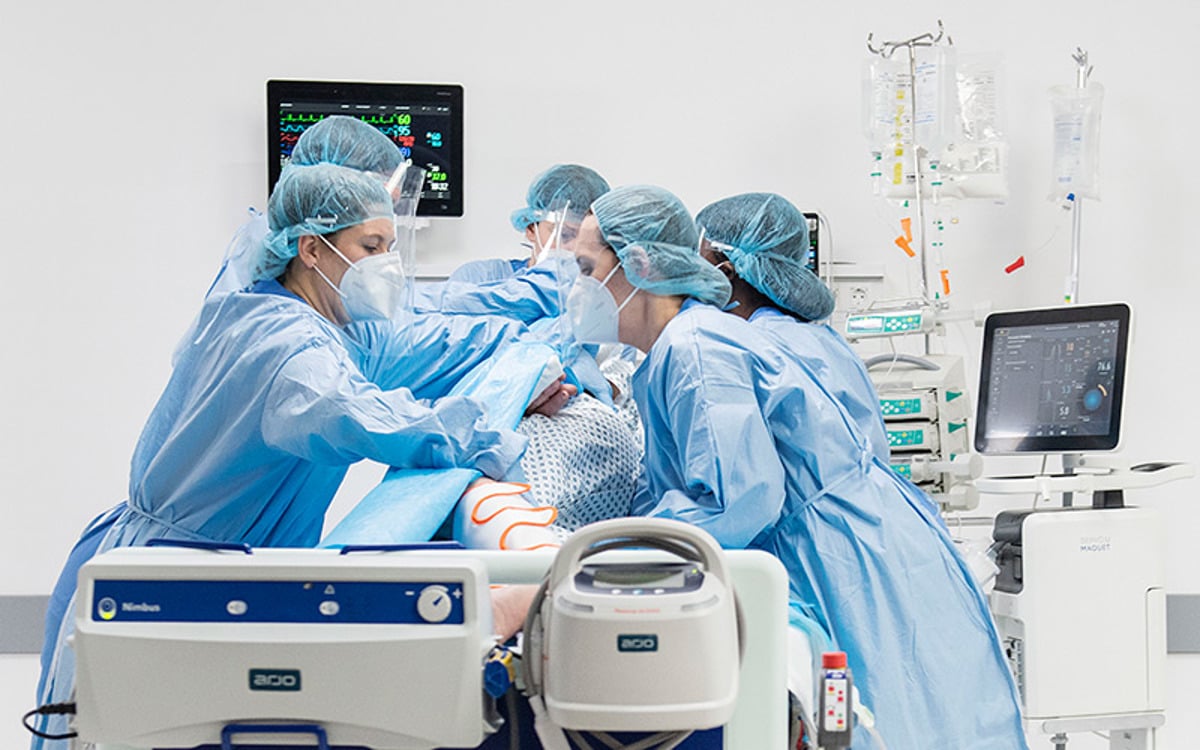
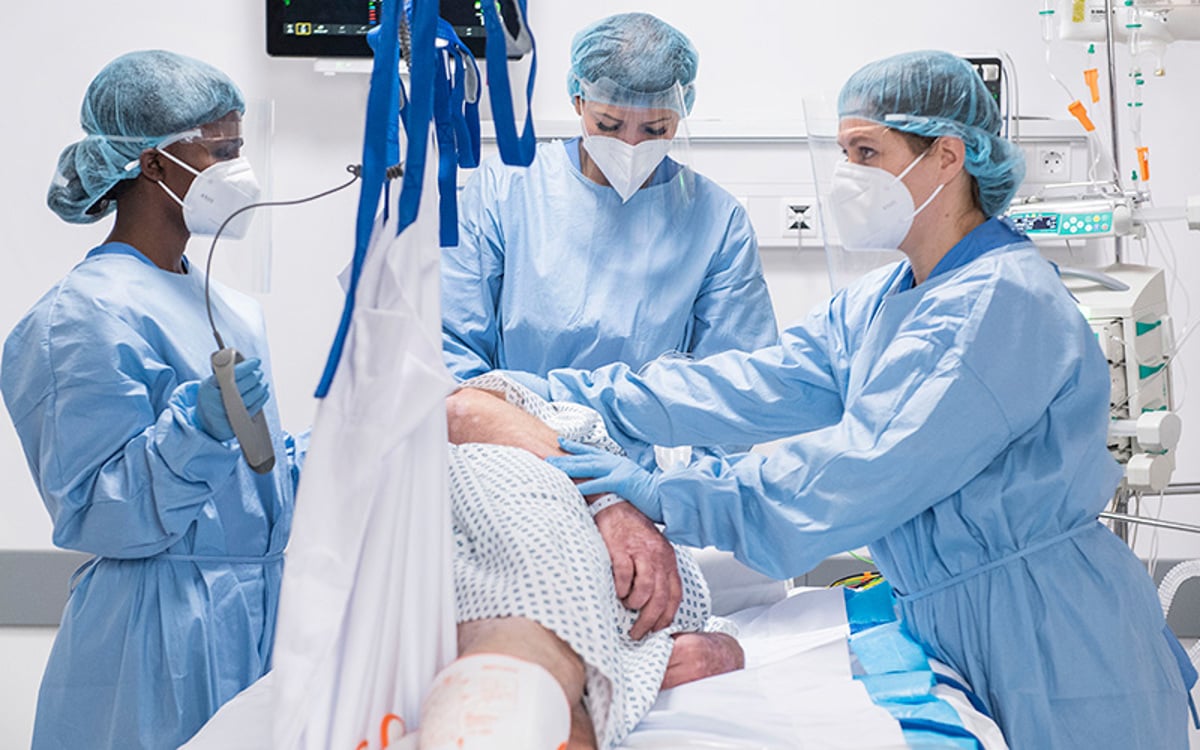
うつ伏せ/仰向けへの体位変換
Prone positioning involves turning a patient onto their chest. This may sound like a straightforward task. However, clinicians appreciate that this can be a complex, labour-intensive manoeuvre that can put both patients and caregivers at risk.
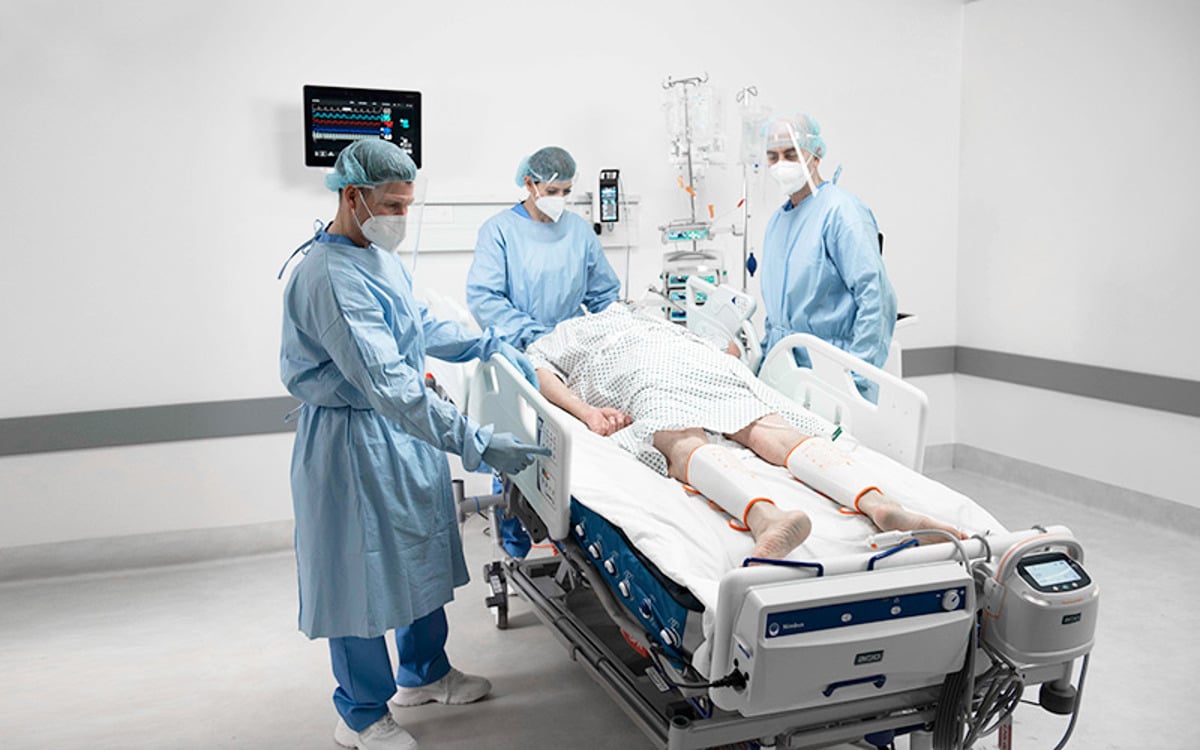
腹臥位
Patients often spend up to 16 hours out of every 24-hour period in the prone position⁵. Such lengthy sessions are associated with an increased risk of pressure injury.⁶
参考文献
- Papazian, L., Aubron, C., Brochard, L., Chiche, J., Combes, A., Dreyfuss, D., Forel, J., Guérin, C., Jaber, S., Mekontso-Dessap, A., Mercat, A., Richard, J., Roux, D., Vieillard-Baron, A. and Faure, H., 2019. Formal guidelines: management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Annals of Intensive Care, 9(1).
- Bamford, P., et al, 2019. Guidance For: Prone Positioning in Adult Critical Care. Intensive Care Society and Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine.
- Richardson et al., 2019. Perspectives on preventing musculoskeletal injuries in nurses: A qualitative study. Nursing Open.
- Wiggermann, N., Zhou, J. and McGann, N., 2020. Effect of Repositioning Aids and Patient Weight on Biomechanical Stresses When Repositioning Patients in Bed. Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society.
- Guerin C, et al, 2013. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med.
- Girard R, Baboi L, et al., 2014. The impact of patient positioning on pressure ulcers in patients with severe ARDS: results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial on prone positioning. Intensive Care Med.
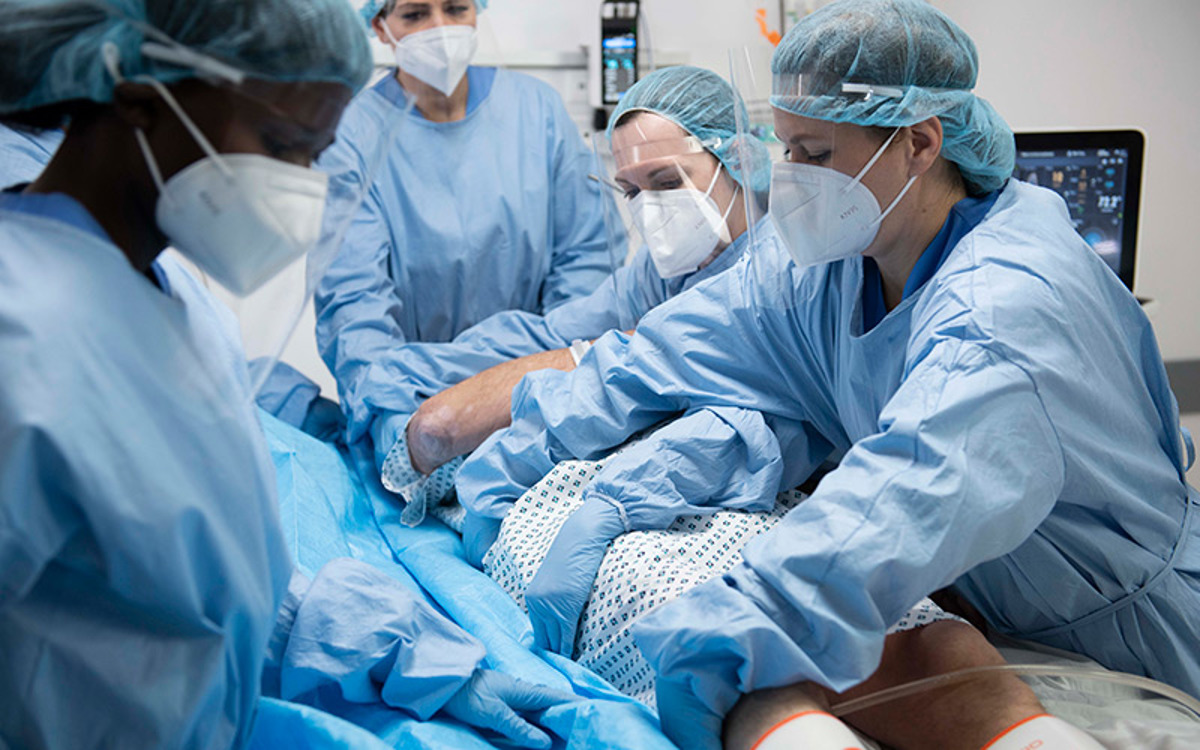



_Product_Node_Hero_Image.jpg)