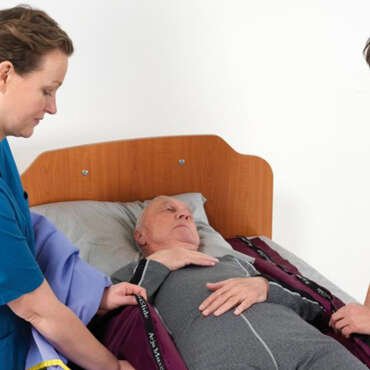
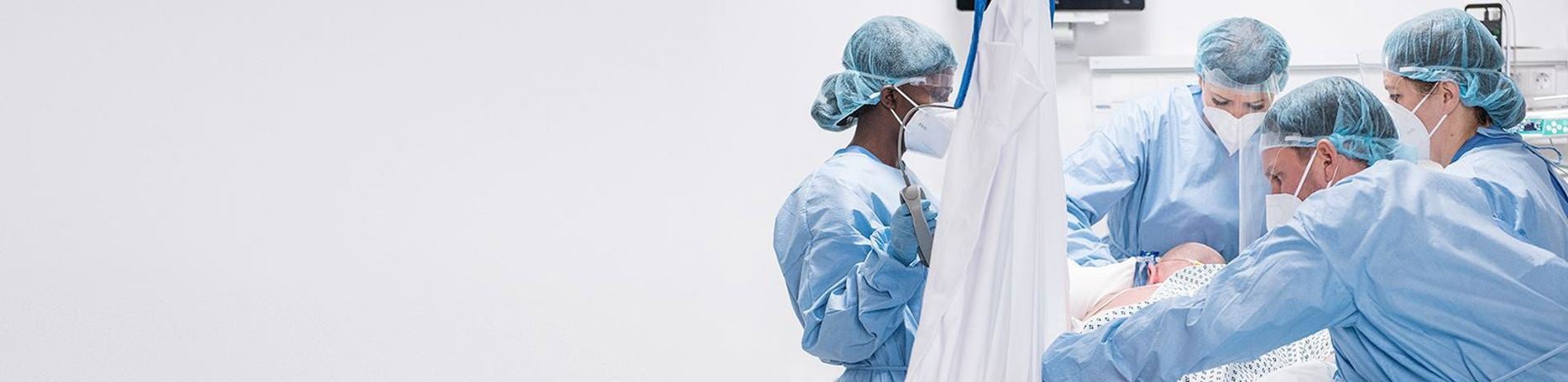
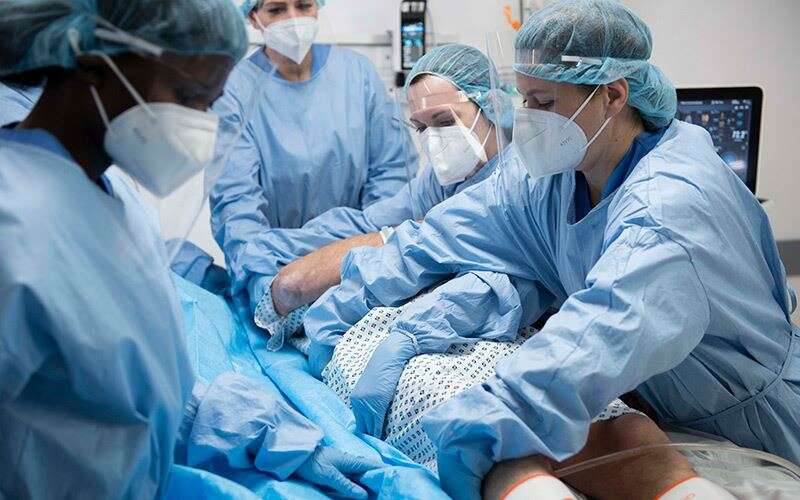
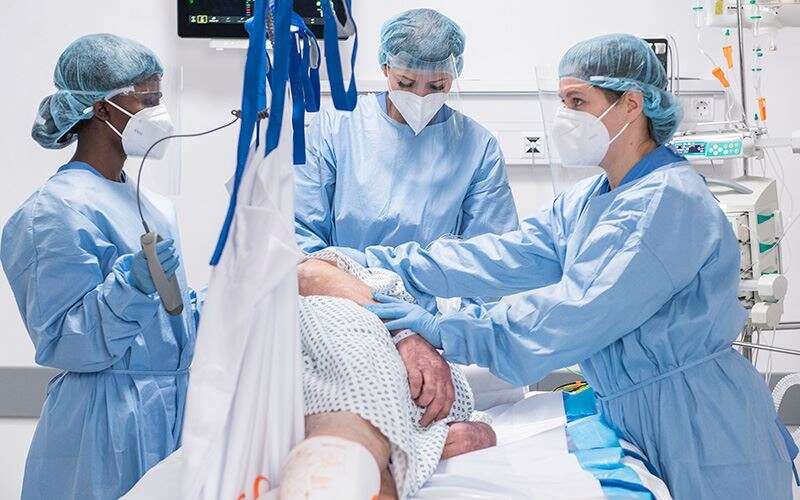
Rotation vers et depuis la position de décubitus ventral
Le positionnement en décubitus ventral consiste à retourner un patient sur sa poitrine. Cette tâche peut sembler simple. Cependant, les cliniciens savent qu'il s'agit d'une manœuvre complexe qui demande beaucoup de travail et qui peut mettre en danger à la fois les patients et les soignants.
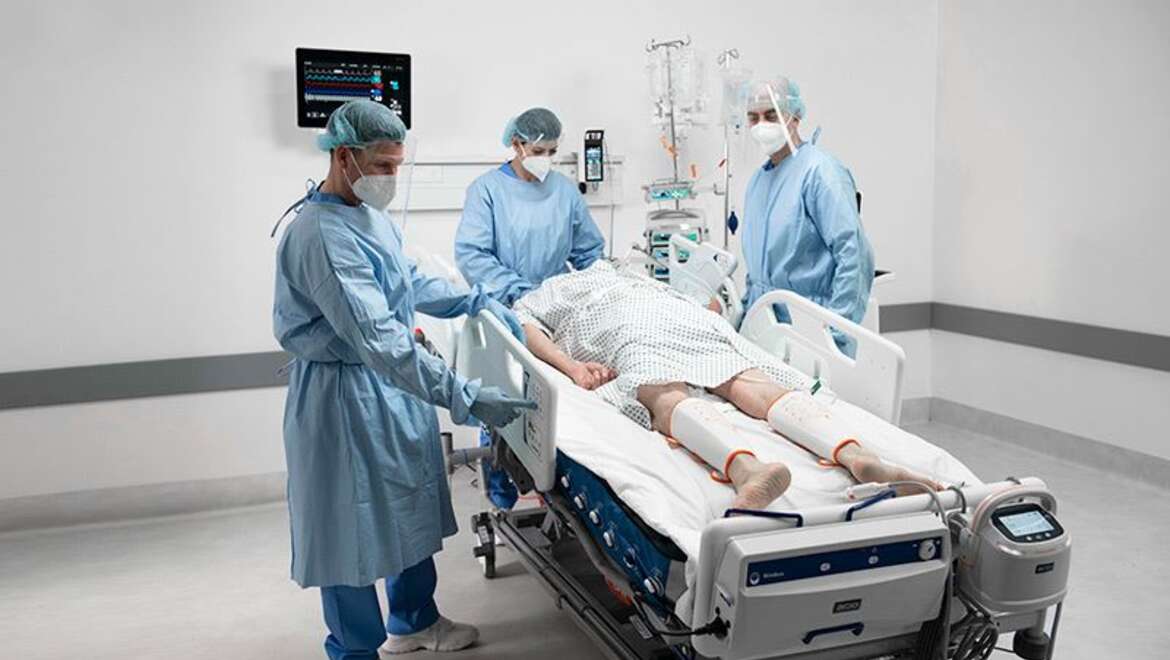
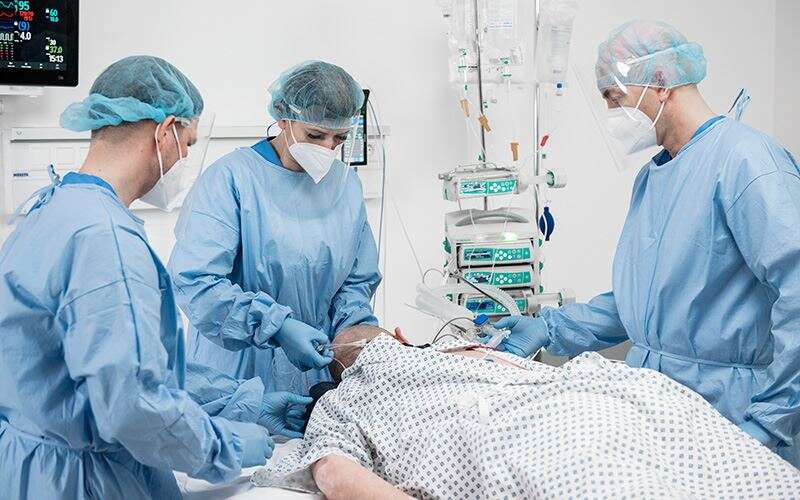
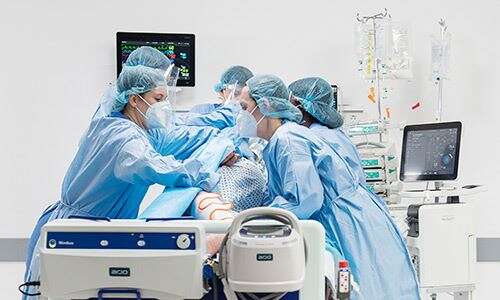
En décubitus ventral
Les patients passent souvent jusqu'à 16 heures sur 24 en position couchée⁴. Ces longues séances sont associées à un risque accru d’escarres.⁵
Références
- Papazian, L., Aubron, C., Brochard, L., Chiche, J., Combes, A., Dreyfuss, D., Forel, J., Guérin, C., Jaber, S., Mekontso-Dessap, A., Mercat, A., Richard, J., Roux, D., Vieillard-Baron, A. and Faure, H., 2019. Formal guidelines: management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Annals of Intensive Care, 9(1).
- Bamford, P., et al, 2019. Guidance For: Prone Positioning in Adult Critical Care. Intensive Care Society and Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine.
- Richardson et al., 2019. Perspectives on Preventing Musculoskeletal Injuries in Nurses: A Qualitative Study. Nursing Open.
- Wiggermann, N., Zhou, J. and McGann, N., 2020. Effect of Repositioning Aids and Patient Weight on Biomechanical Stresses When Repositioning Patients in Bed. Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society.
- Guerin C, et al, 2013. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med.
- Girard R, Baboi L, et al., 2014. The impact of patient positioning on pressure ulcers in patients with severe ARDS: results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial on prone positioning. Intensive Care Med.
_Product_Node_Hero_Image.jpg)